This post is part of a series covering the unbundling and automation of the restaurant business. You can view the full interactive map with more than 50 startups here.
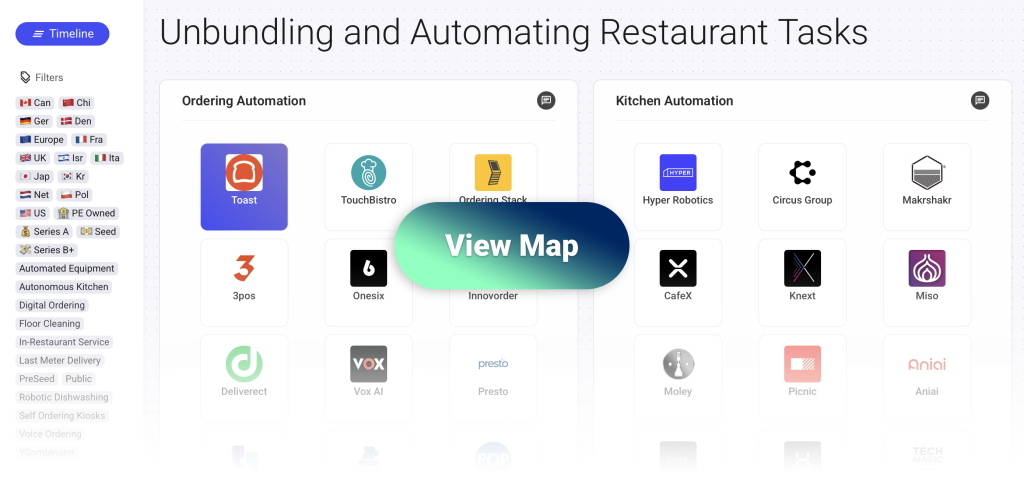
Automation, robotics and AI are reshaping every step of restaurant work, from the moment a customer orders to the way kitchens prepare food, deliver dishes, clean tables and manage ingredients. This deep dive shows a concrete view of the emerging technologies that take over repetitive tasks will help restaurants at a time when fewer people want to do these roles.
Kitchen Automation
Kitchen automation covers machines and robotic systems that assist with or fully take over food preparation tasks in the kitchen. They handle repetitive or “dangerous” work so staff can focus on supervision and quality.
How automation, robotics and AI are changing it:
Robotic arms cook, grill, fry or assemble food with high consistency. Fully automated kitchen units prepare entire dishes from raw ingredients to plated meals. AI optimizes timing, temperature and workflow so the overall kitchen output becomes faster and more predictable.
Automated Kitchen Equipment:
- Machines that assist human cooks by handling tasks such as frying, mixing or cutting.
- Improve consistency and speed while reducing physical strain on staff.
- Work alongside chefs rather than replacing the entire workflow.
Fully Autonomous Kitchen Systems:
- Integrated robotic units that prepare complete dishes from start to finish, until delivery to the customer (for some).
- Use ingredient cartridges, smart dispensers and robotic arms to handle all steps.
- Allow fully autonomous restaurants to produce menu items with no human intervention.
14 Startups Automating Kitchen Work
🇮🇱 Isr – 💵 Seed – Autonomous Kitchen
What they do:
- Hyper builds fully autonomous fast food kitchens packaged inside self contained units that cook, assemble and package meals without human staff.
- The robotic system handles every stage of preparation from raw ingredients to finished products using sensors, automated dispensers and AI guided cooking processes.
- Food formats supported include pizzas, burgers, bowls and salads which gives operators flexibility across several cuisine types.
- Deployment is fast because the kitchen arrives as a ready to operate module that only needs stocking before service can begin.
- Hyper provides a turnkey service that includes operations, monitoring and maintenance which allows brands to expand without running their own kitchen teams.
Company specificities:
- A container based plug and play design makes these robotic kitchens easy to place in parking lots, malls, roadside stops or other non traditional locations.
- Full automation eliminates the need for back of house labor which reduces operating costs and removes scheduling and turnover issues.
- Each unit is self contained which makes scaling straightforward since new sites can be added without long construction timelines.
- Robotic processes offer consistent portioning, improved hygiene and reduced waste which supports both food safety and operational efficiency.
🇩🇪 Ger – 🇪🇺 Europe – Autonomous Kitchen – Public
What they do:
- Circus Group creates fully autonomous food production systems that cook, assemble and plate meals without human chefs.
- Their main product, the CA1 robot, manages ingredient storage, cooking, plating and heated pickup to deliver ready meals on demand.
- The solution fits supermarkets, airports, campuses, corporate spaces and other locations where a traditional kitchen would not be practical.
- Orders and meal production can be triggered through touchscreens or voice interfaces while AI manages cooking processes, inventory, hygiene and quality.
- The company aims to provide affordable and consistent meals while reducing the labour and operational challenges common in food service.
Company specificities:
- A proprietary ecosystem that includes robotics, software and an AI layer allows Circus to manage cooking, logistics and operations in a fully integrated way.
- CA1 has a compact footprint and can produce high volumes of meals, enabling deployment in retail and transit spaces rather than requiring full kitchen infrastructure.
- Smart ingredient silos, sensors and AI forecasting reduce waste, maintain hygiene and support continuous production.
- After industrialising its hardware, the company is focused on scaling distribution and positioning autonomous kitchens as a new standard for prepared food.
🇪🇺 Europe – 🇮🇹 Ita – Autonomous Kitchen
What they do:
- Makr Shakr builds robotic bartenders and drink making systems that can mix, shake and serve cocktails or other beverages on demand.
- Customers place orders through a digital interface and the robot prepares each drink by selecting ingredients, mixing them and adding garnishes with precise movements.
- The system can handle high order volumes which suits nightlife venues, clubs, events and entertainment environments where speed and consistency matter.
- A strong show element is part of the experience since the robotic arms create a visually engaging performance while preparing drinks.
- Users can customise recipes or create their own drinks which adds an interactive and personalised dimension to the experience.
Company specificities:
- The robots are engineered and produced by Makr Shakr in Italy which results in a blend of advanced robotics and refined industrial design.
- Their systems support a large number of ingredients at once which allows venues to offer a broad drink menu with many variations.
- The company positions the solution as an extension of hospitality workflows rather than a replacement for human bartenders which aligns with venues seeking novelty and efficiency.
- The mix of automation and theatrical presentation helps venues differentiate themselves and offer a unique customer experience.
🇺🇸 US – 💵 Seed – Autonomous Kitchen
What they do:
- Cafe X operates fully autonomous robotic coffee bars that brew and serve drinks without the need for human baristas.
- Customers place their orders through a mobile app or on site kiosk and pick up their drink from automated pickup bays.
- The system handles grinding, brewing, mixing and dispensing with consistent quality for every beverage.
- It is designed for high traffic locations such as airports, malls, offices and transport hubs where speed and reliability matter.
- Operators use a digital console to manage menu items, pricing, inventory and remote monitoring across locations.
Company specificities:
- Hardware and software are developed in house which ensures tight coordination between robotics, ordering flow and operational controls.
- The robot prepares drinks quickly with reliable consistency which supports high throughput during peak hours.
- Automated pickup windows create a contactless experience that reduces queues and improves order handling efficiency.
- Remote analytics give operators insight into drink popularity, stock levels and performance which helps optimise multi location operations.
🇩🇪 Ger – 🇪🇺 Europe – Autonomous Kitchen
What they do:
- FutureCafé is a fully automated café concept where robotic arms prepare coffee, tea and selected snacks without human baristas.
- Customers order through a digital interface and the system handles preparation, dispensing and serving with consistent quality.
- The setup supports a mix of hot and cold beverages along with grab and go snacks which turns a very small footprint into a complete café offer.
- A compact layout, often around nine square meters, allows installation in offices, travel hubs, retail environments or locations where a traditional café cannot fit.
- The café is designed to operate around the clock with minimal human intervention thanks to sensors, robotics and automated hygiene routines.
Company specificities:
- The system is engineered and manufactured in Germany which brings industrial grade reliability and attention to quality.
- Strong space efficiency makes it possible to run a full café experience in areas where space is scarce or costly.
- Automation covers more than drink preparation, including snack distribution, hygienic handling and basic inventory management for a seamless grab and go service.
- The model addresses staffing shortages by providing consistent service without baristas, making it suitable for high traffic or unattended locations.
🇺🇸 US – 💸 Series B+ – Automated Equipment
What they do:
- Miso Robotics develops AI powered kitchen robots designed to automate repetitive and labor intensive cooking tasks in commercial kitchens.
- The flagship system, Flippy, takes over fry station duties by managing cooking times, basket movements and product handling with consistent precision.
- Their technology stack uses computer vision and real time AI to recognise food items, adjust cooking routines and monitor equipment performance.
- Restaurants can adopt the robots through a subscription model which reduces upfront capital requirements and simplifies maintenance.
- The systems help quick service restaurants increase throughput, maintain quality across shifts and reduce exposure to hot oil and hazardous kitchen environments.
Company specificities:
- Miso holds a substantial portfolio of patents covering robotics control, automation logic and computer vision which strengthens its technological moat.
- The robots are designed to retrofit into existing kitchen layouts so operators do not need to rebuild or redesign their back of house setup.
- The Kitchen AI platform gathers data across stations and provides insights into uptime, cooking patterns and fleet performance which supports operational optimisation.
- Strategic partnerships with major industry players give Miso access to strong distribution networks and advanced AI hardware ecosystems.
🇪🇺 Europe – 🇬🇧 UK – 💵 Seed – Automated Equipment
What they do:
- Moley Robotics develops a fully robotic kitchen system where articulated robot arms prepare meals by replicating the movements of professional chefs.
- The kitchen includes integrated appliances, storage and cookware so users can select recipes from a digital catalogue and have them cooked automatically.
- Meal preparation covers the full workflow from ingredient handling to cooking, plating and basic cleaning which turns complex recipes into a simple guided process.
- A smart-kitchen version is available for assisted cooking, offering automation for selected steps rather than full autonomy.
- The product targets high end residential customers and luxury homes seeking a chef-level cooking experience without needing culinary skills.
Company specificities:
- The company pioneered the concept of a robotic kitchen by combining robotics, motion capture, sensors and appliance integration into one coordinated system.
- Robot arms are designed to work with standard pots, pans and utensils which allows a broad range of dishes rather than a fixed menu.
- A large recipe library is available and professional chef techniques can be reproduced with consistency by the robot.
- Users can switch between automated mode and manual mode which makes the kitchen flexible for different cooking preferences.
🇺🇸 US – 💵 Seed – Automated Equipment
What they do:
- Picnic Works builds automation equipment for commercial kitchens with a focus on a pizza assembly station that automates sauce spreading, cheese dispensing and topping placement.
- The system produces pizzas at high speed which helps kitchens handle large volumes with fewer staff.
- Installation is simple because the station is designed to fit into existing kitchen layouts without major construction or special utility needs.
- Automation improves consistency and reduces errors in pizza preparation which leads to more predictable product quality.
- The solution is used in pizzerias, fast service restaurants, stadiums, campuses, convenience stores and other venues that need reliable high volume output.
Company specificities:
- A modular design allows operators to choose different configurations depending on their needs such as basic sauce and cheese or full topping automation.
- Labor requirements drop significantly since repetitive prep tasks are handled by the machine which frees staff for other duties.
- The system reduces food waste by dispensing precise quantities of ingredients which helps control costs and improves sustainability.
- Picnic Works often offers automation as a service which includes setup, support and optional integrations like pickup lockers for a more complete automated workflow.
🇰🇷 Kr – 💵 Seed – Automated Equipment
What they do:
- Aniai builds a robotic grill system that automates cooking burger patties in commercial kitchens.
- Sensors and AI track temperature, surface colour and doneness so each patty cooks to a consistent standard.
- The grill cooks many patties per hour which supports restaurants that deal with heavy rush periods.
- Automated flipping and timing reduce staff workload and remove one of the most repetitive kitchen tasks.
- Multi-location operators benefit from uniform cooking quality across restaurants without depending on individual staff skills.
Company specificities:
- The grill uses a dual-sided cooking system that cooks both sides of the patty at once which boosts speed and throughput.
- A cloud connected AI layer monitors cooking performance in real time and provides analytics that help operators control quality and efficiency.
- Automation reduces variability caused by staff turnover and ensures consistent results which is important for strong brand standards.
- The product directly addresses labour shortages in kitchens by taking over a demanding and time-constrained task while staying compact enough to retrofit into existing setups.
🇺🇸 US – Automated Equipment
What they do:
- Chef Robotics builds AI powered robotic systems that automate meal assembly for food manufacturers and large kitchen operations.
- Robots portion ingredients and deposit them into trays or containers with consistent precision, mimicking human assembly line movements.
- A software platform allows the robots to adapt to many recipes, ingredient types and tray layouts which supports a wide range of meal formats.
- High throughput capability helps producers scale output and reduce reliance on manual labour.
- Customers include ready meal producers, large catering operations and food companies needing reliable, repeatable assembly at volume.
Company specificities:
- The system is modular and fits directly into existing conveyor based production lines which avoids major facility redesign.
- Computer vision and AI allow the robots to recognise ingredients, handle variation and portion accurately even when items are irregular or trays shift slightly.
- A multi deposit mode increases productivity by enabling several tray deposits per movement which brings robot output closer to or above human rates.
- A robotics as a service model lowers upfront investment and helps food manufacturers adopt automation without significant capital expenditure.
🇺🇸 US – 💸 Series B+ – Automated Equipment
What they do:
- Hyphen offers an automated makeline that assembles bowls, salads and similar meals by portioning and dispensing ingredients automatically.
- Digital orders from apps, delivery platforms, kiosks or drive thru flows directly into the system so meals are produced without manual assembly.
- The equipment supports high throughput and can prepare many meals per hour which helps restaurants handle peak demand.
- Built in software manages recipes, inventory, ingredient usage and forecasting which improves consistency and cost control.
- The solution fits restaurants, ghost kitchens, catering operations, campuses and retail food outlets that need fast and consistent meal production.
Company specificities:
- The makeline combines robotics and kitchen grade software to deliver precise portioning and reduce waste while maintaining consistent quality.
- Its modular design fits into existing kitchen spaces and uses standard containers so operators do not need heavy renovations.
- Deep tracking of ingredient usage, throughput and performance gives operators real operational visibility and data driven optimization.
- The system works for both batch production and individual made to order meals which gives flexibility across many types of foodservice operations.
🇯🇵 Jap – Automated Equipment
What they do:
- TechMagic develops cooking robots that automate tasks such as stir frying, boiling and frying to reduce repetitive and intense work in restaurant kitchens.
- Their systems handle ingredient dispensing, sauce application, temperature control, stirring, flipping and in some cases cleaning so the full cooking flow becomes automated.
- The company serves restaurants, central kitchens and food production facilities that need consistent output and relief from labour shortages.
- Robots can produce meals with stable quality by following precise time and heat profiles which helps multi location operators maintain uniform taste.
- TechMagic also explores robot first restaurant formats that rely heavily on automation to deliver meals at scale with less staffing.
Company specificities:
- The robots combine hardware with AI and machine learning to reproduce skilled chef techniques with repeatable precision.
- A modular lineup covers different cooking methods so operators can choose systems suited to their menu rather than adopting a single generic robot.
- TechMagic positions its technology as core infrastructure for the future of food service aimed at solving structural labour and cost pressure rather than offering a niche gadget.
- Real world deployments show that the robots function in active kitchens which demonstrates the maturity of both the cooking hardware and the control software.
🇺🇸 US – 💸 Series B+ – Autonomous Kitchen
What they do:
- Botrista builds automated beverage machines that prepare crafted cold drinks such as boba teas, iced coffees, smoothies, lemonades and shakes with little staff involvement.
- The system dispenses and mixes ingredients like powders, liquids and syrups with precise recipes so each drink is consistent in taste and portioning.
- It produces drinks very quickly which makes it useful for high-traffic venues that want to add a modern beverage offering without training specialised staff.
- Operators can offer a large menu of recipes and seasonal combinations, making it easy to adapt to trends without slowing down operations.
- The solution suits cafés, campus dining halls, convenience stores, fast casual restaurants and ghost kitchens that want high-margin beverages without building a full drink preparation station.
Company specificities:
- The machine has a compact footprint so venues can install it without major layout changes, which helps in small spaces.
- Data and analytics help operators understand drink popularity and adjust menus to local demand which improves sales performance.
- Using concentrated or prepared ingredients reduces storage needs and waste while keeping drinks consistent across shifts.
- The platform is built for quick rollout and easy scaling, as new recipes can be added without retraining staff or changing equipment workflows.
🇨🇦 Can – Autonomous Kitchen
What they do:
- Chef Jasper builds and operates robotic kitchens that can prepare fresh meals automatically from ingredient handling to cooking and plating.
- The service is delivered as a turnkey package that includes robotics, menu planning, order software, inventory tools and on-site staff for upkeep.
- Their kitchens support a wide repertoire of dishes ranging from simple recipes to gourmet plates along with meals adapted to dietary or medical needs.
- Automation helps clients offer consistent meals at lower operating cost and with less dependency on kitchen labor.
- Typical customers include senior living facilities and care institutions that need reliable, nutritious meal production every day.
Company specificities:
- The solution bundles hardware, software and human oversight which removes the need for clients to assemble different components themselves.
- Menu flexibility is greater than in many automated kitchen systems which allows Chef Jasper to serve varied cuisines and specialized diets.
- Dietary personalization is built into the workflow which supports environments with strict nutritional or medical meal requirements.
- A subscription model replaces large initial investments and makes costs predictable and comparable to traditional food service arrangements.